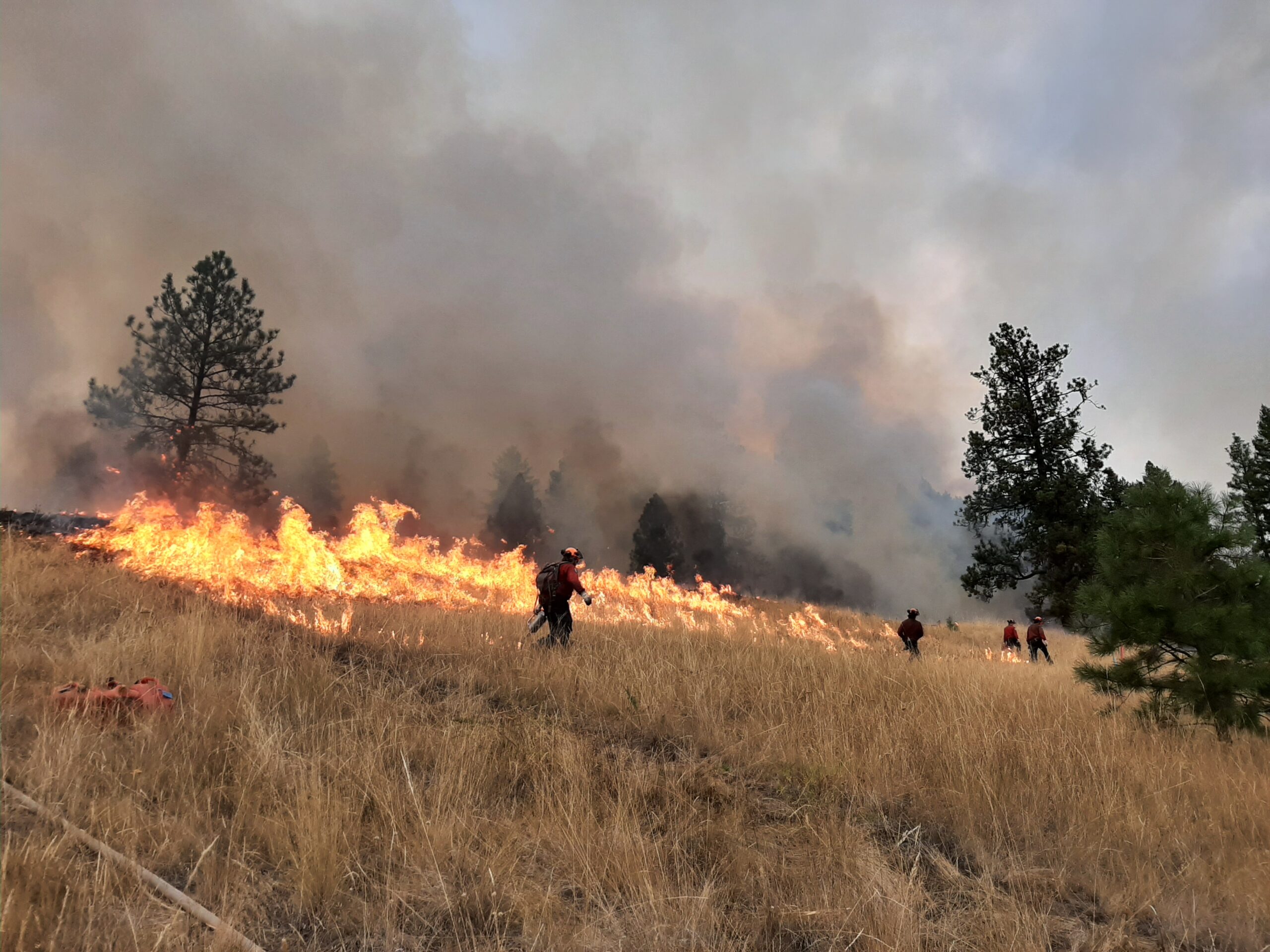
KOOTENAY REGION, B.C. – many Indigenous communities, municipalities, regional districts, woodlots, and community forests have taken action in the last few years to protect their communities from wildfire. Using funding from the Forest Enhancement Society of BC (FESBC) these project partners first create a Community Wildfire Protection Plan (CWPP) or a Community Resiliency Protection Plan (CRPP), which identifies the location of buildings, communications infrastructure, water, power, safe places, and emergency escape routes. Then based on the amount of woody fuel risk, the CWPP or CRPP prioritizes which treatments should be done first.
“The key goals of the Community Wildfire Resiliency Planning process are varied,” said Gord Pratt, RPF, Operations Manager FESBC. “Goals include increasing communities’ capacity and understanding of wildfire risk, fostering greater collaboration across administrative boundaries, and being more responsive to the needs of different types of communities throughout B.C. in terms of their size, capacity, and the threats they face.”
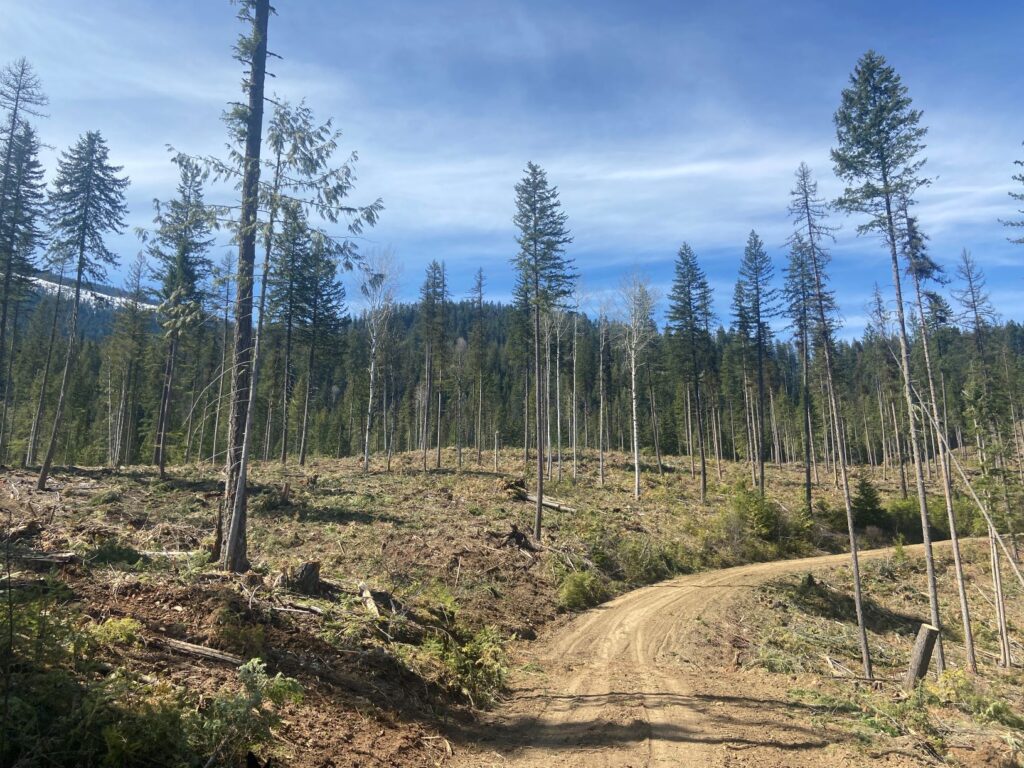
Wildfire risk mitigation planning and treatments can be quite different depending on where in the province a project is located.
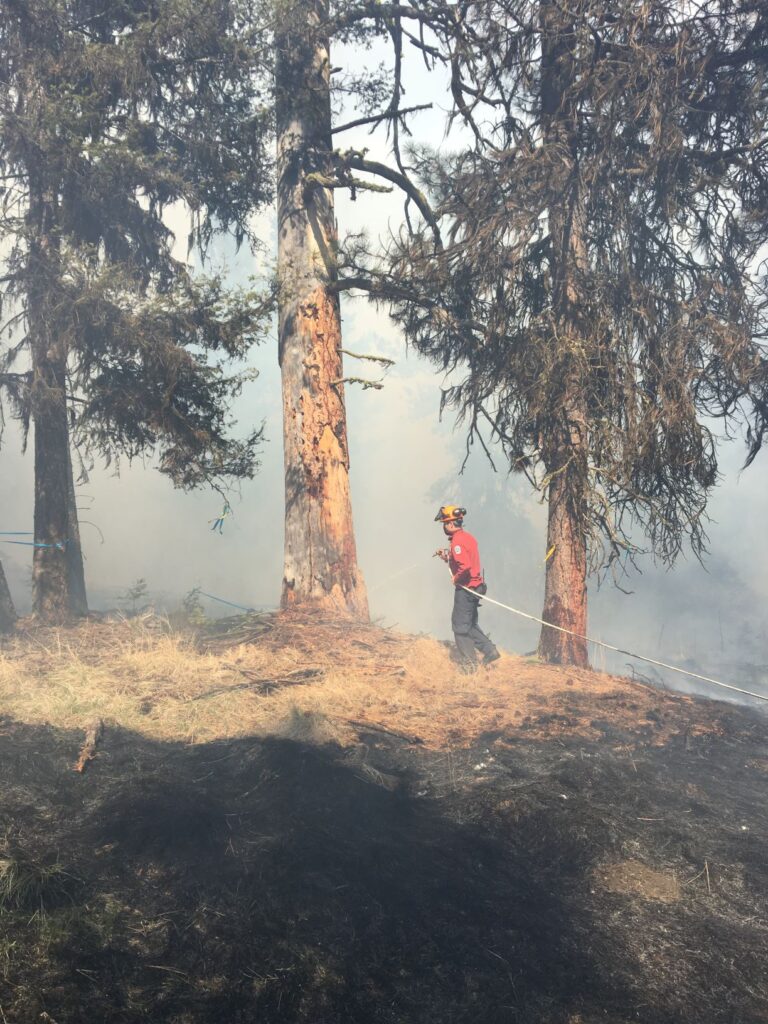
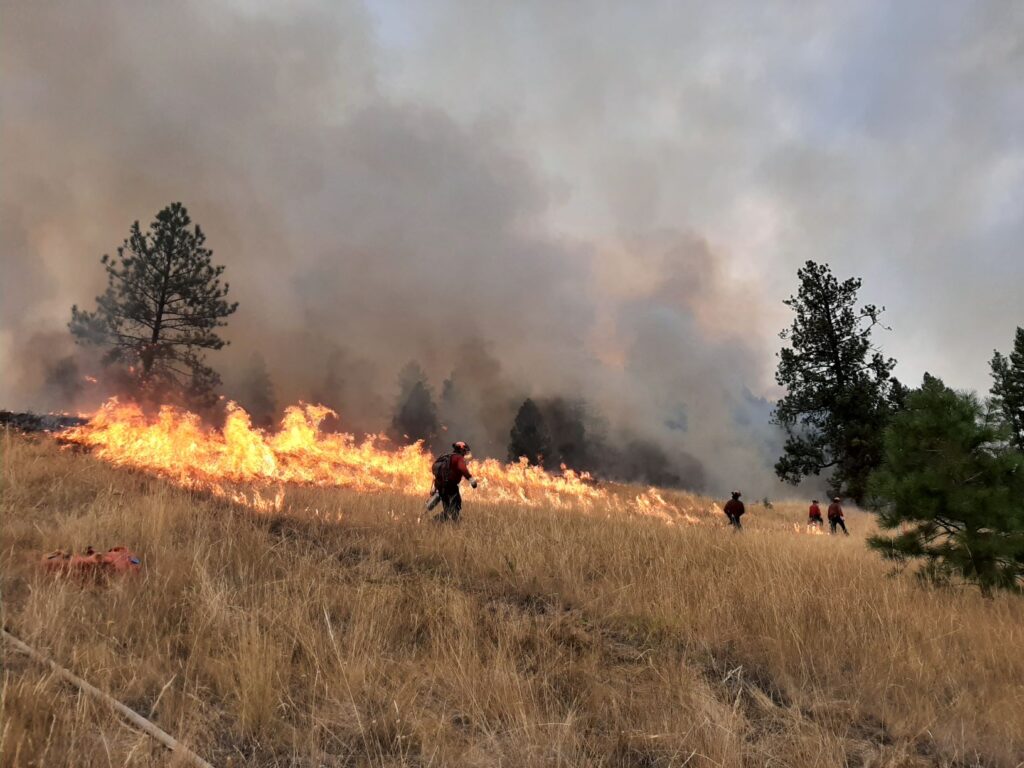
“Wildfire treatments will often space trees far apart and remove low branches in order to keep a fire on the ground and to reduce the amount of wood in the forest, so it doesn’t burn as hot. This makes it easier to fight the fire,” said Steve Kozuki, RPF, Executive Director of FESBC. “But every community is different, and some communities have chosen to encourage the planting of broad-leaved trees in specific areas because they are often more fire-resistant.”
Since inception, FESBC has provided nearly $57 million to fund 124 wildfire risk reduction projects. These projects have not only reduced wildfire risk to 120 communities and rural sub-divisions but have generated an estimated 483 jobs (full time equivalent jobs created) and 43 of these projects have involved, or have been led by, First Nations.
“We wanted to share with residents in the region some of the wildfire mitigation work FESBC has funded in the area,” said Kozuki. “We’ve enclosed descriptions of 40 projects in the Kootenay region to provide a deeper look at the important work that has been done. Although many of the project leaders are currently working on fighting fires and unfortunately not available for interviews at this time, our team at FESBC is ready to share additional project details or answer questions media or citizens may have.”
In addition, when it comes to wildfire mitigation work, the BC government has a wildfire risk reduction funding program called Community Resiliency Investment Program (CRI) which is a partnership with the First Nations Emergency Services Society, the Union of BC Municipalities, the Ministry of Forests, and others, including FESBC. The CRI Program has been spear-heading the FireSmart initiative to educate homeowners about actions they can take to protect themselves, such as cleaning gutters and removing flammable materials outside of homes and businesses. Other funding programs to reduce wildfire risk are administered by the Columbia Basin Trust and the BC Community Forest Association.
For information or an interview regarding these projects, contact:
Steve Kozuki, Executive Director | skozuki@fesbc.ca | 250.819.2888